A Simplistic Guide, Part I
Are you new to 3D? Do you ever wonder what the fuss is all about? Want to know how this new technology can help you grow your business? This article gives you a crash course of 3D rendering. In this two-part primer, we lay down the facts straight and simple to help you get acquainted with the technology and how and where it fits in with your vision of the future.
What is 3D Rendering?
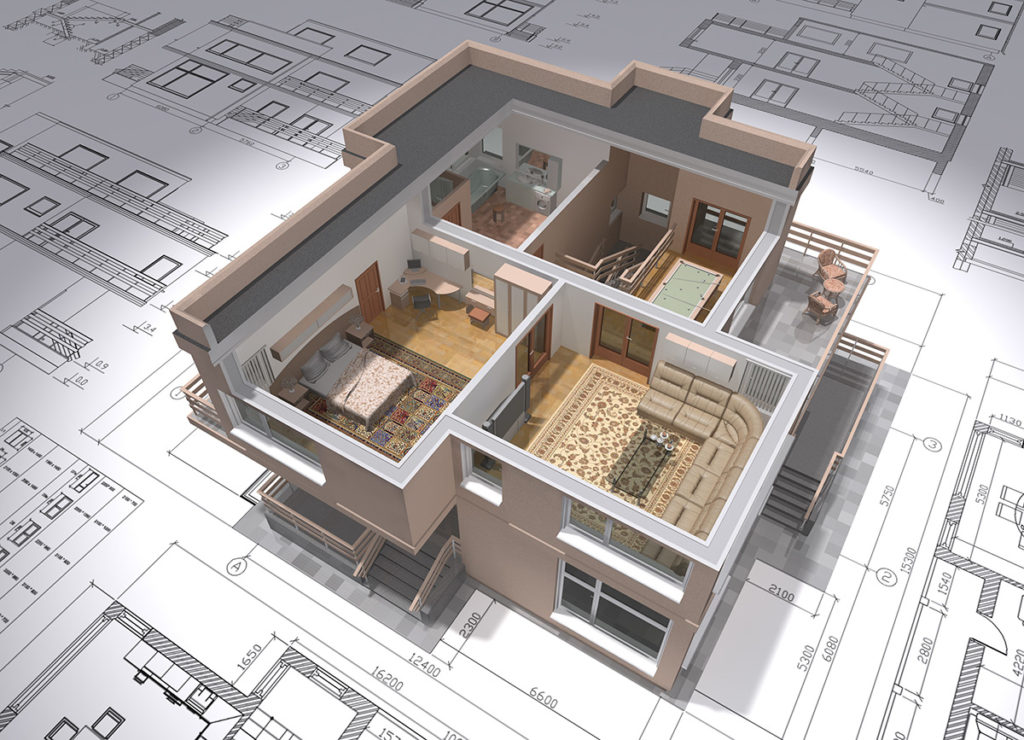
To put it simply, 3D rendering is basically the process of producing an image based on three-dimensional data stored within a computer.
It’s similar to photography except that you have to completely create the image and the scene on the photo.
To be able to do this, two processes are involved: modeling and rendering.
Modeling involves turning 3D wireframe models or skeletal representations of real-world objects into 2D images on your computer. This has to be manually done and requires plenty of work before the 3D rendering process can begin. But it also allows the designer full creative control of the 3D output.
The rendering process aims to depict an object or a scene in a specific, often lifelike or photorealistic perspective by simulating various lighting, shadows, atmospheres, textures, colors, and other optical effects.
Post-production work involving aesthetic touches uses various photoshopping softwares to produce high-quality 3D visualizations.
A Brief History
We could all credit this wondrous technology to the genius of a man named William Fetter. Back in the 60s while working with Boeing, he was tasked to augment the efficiency of space in airplane cockpits. Fetter experimented with depicting the human form via computer-generated orthographic projection, eventually calling the resulting output a computer graphic.
Fetter’s little curious adventure spawned a whole industry, eventually leading to the development of Computer-Aided Design (CAD), and the rest is history.
Today, you can see all sorts of products using 3D technology. Animated films and video games build entire worlds out of pure computer graphics and sheer human ingenuity. 3D effects are often used in film. Industries such as architecture and design, primarily, are reaping the magnitude of its benefits. Its huge capacity to aid and augment human experience is a beacon call for other business sectors to explore its potential.
Realism: Photorealistic Vs Colored
Depending on the type of the project or specification of a client, a 3D output can be viewed in photorealistic or colored views.
Photorealistic means the photo or image appears to be life-like, as though captured by a camera or seen by the naked eye.
Colored views are more graphical and the level of realism is usually presented in more picture-like coloring and shading.
Color and Material Study
Found to be very valuable among real estate businesses, 3D studies on color and material variations make staging easy, allowing interior designers to experiment with multiple design prospects and choose the most aesthetically workable design option possible.
Lighting Study
The property’s exterior aesthetics largely depend on location and lighting. By conducting various lighting studies using variant light types, color, and intensity, 3D tech can simulate daylight and nighttime atmosphere to see how finished projects would look like.
Photomontage
Photomontage is a feature that allows the designer to integrate a design element into an existing one. For example, if you’re working on a new apartment complex and you want to know how it would look like with the rest of the neighborhood, a photomontage places a photorealistic 3D image of the project and merge it to a photograph of the site to evaluate whether your design choices are adequate and tenable.
Types of 3D Visualizations
With all these being discussed, it should be noted that the 3D renderings do not exclusively come in photorealistic 3D images or photomontages.
Your 3D visualization can also be made as 3D walkthroughs or 3D animations so you can also interact with the design as if in real life. This is especially exciting with the advent of virtual reality.
3D is basically a technology at its infancy. Notwithstanding, it’s managed to disrupt the way modern humans interact with our own creativity and use it as a tool to feed the exponentially increasing pace of human advancement.
Stay tuned for the second part of this primer to learn more about benefits of 3D Visualization.