A 3D Printer is perhaps one of the most revolutionary inventions of the 21st century. Integrating 3D tech into the work process has helped many modern companies reduce their turnaround times, inspire creative work, and produce multiple iterations of a product in the cheapest and most efficient way possible. But how exactly is it used by industries today?
This article looks into the most innovative applications of 3D technology and how companies use them to increase their competitive edge in a highly-competitive market.
Product Design and Development
In the traditional way of doing things, developing products usually take weeks to months, depending on what the product is. Fine-tuning the product takes multiple redesigns and it’s a painstaking process when you constantly have to produce multiple prototypes to reflect the changes.
With the advent of 3D tech where changes are made via software and prototypes can be printed in a jiffy, the production of prototypes is significantly reduced, usually by more than half the time it takes to create them through the conventional process.
Because changes are immediate, product evaluation and deliberation can be done sooner and so is the product launch. All these can be done at a fraction of the budget that it costs to do them the way they used to get done.
Assistance in Manufacturing
Tools are vital in the workplace. Any missing tool can halt the production process, thereby sacrificing cost. In the business arena, one cannot afford delays. 3D tools serve as backup, if not become the main pipeline through which products are assembled and work gets done.
If you need tools and fixtures instantaneously, 3D tech and fill the need in no time. But churning out tools on demand is not the limit of how 3D tech can work in the manufacturing setup.
3D printing ensures product quality, provide better product organization, and ensure dimension precision. Not to mention it allows you to create custom-made molds and patterns that can be a game-changer and hasten things up when integrated into your workflow.
When it comes to end-use parts, you can use your 3D printer to produce a small volume of custom, one-off parts, print replacement units, and even de-centralize your manufacturing process by printing products or parts where they are needed.
3D Architectural Renders
No other industry demonstrates the ingenuity of 3D design and its processes more than Architecture. From designing a building to staging interiors or visualizing the construction frames to providing a virtual reality 3D experience, 3D tech showcases the entirety of how 3D can be used and what it can do.
3D architectural rendering breathes life into photorealistic scenes. Concept models can be printed quickly. Architects can not only provide better presentations that are perhaps enhanced with virtual reality systems but also product or print to-scale models of their designs, doing away with the traditional 2D blueprints or manually-produced mock-ups. The renders help refine the details of the design to needle-like precision. And if there are changes to the design, they can be communicated to all departments concerned before they can cause expensive errors in actual construction.
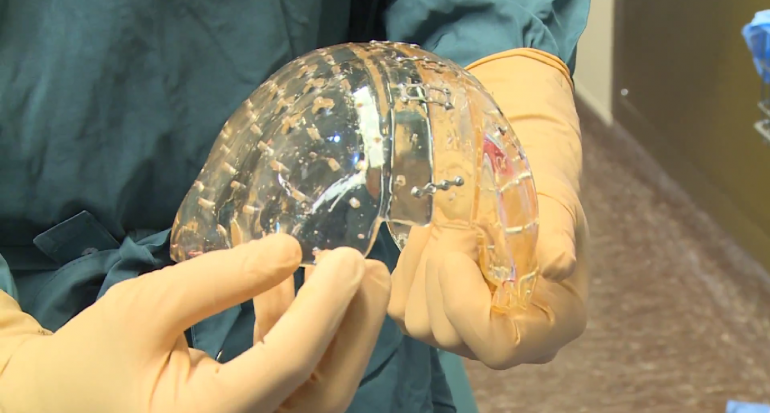
Assistance in Healthcare
Surgical planning is made easier by bringing patient scans to life so that medical professionals can conduct adequate study of the required procedure before operations take place. These will also help them communicate the situation to the patients. Consequently, these tools can be used to effectively train medical personnel without the need for organic subjects.
As far as instrumentation is concerned, the medical industry has been one of the very first benefactors of 3D-printed medical instruments and tools, which makes it possible for them to print tools on demand or use these instruments for research purposes.